Welcome to a new edition of The Finance Gem 💎
weekly strategic finance gems to accelerate your career and grow your business
This Week’s Strategic Finance Insights
You’re probably using EBITDA wrong
10 Business Finance Strategies
EBITDA is not Cash Flow
Costs vs. Expenses
13 Best Business Books
Let’s dive in!
For a limited time, take $25 off $125+ or $50 off $200+ orders in my digital store. Head over to www.oanalabes.com to get my viral cheat sheets, checklists and infographics in full resolution, for posters or gifts. Use coupon codes 9C4UXH (for $25 off) or 4T7EQ9 (for $50 off) at checkout. Expires October 7.
For custom orders please get in touch.
This newsletter edition is brought to you by Shield App. Whether you are growing your LinkedIn account, or you simply want to keep track of your LinkedIn content and be able to search and find your posts in seconds, this tool is going to make your life so much better. Not only will Shield App help you sort your posts by most views, comments or likes, but it also comes with a free trial so you can try it at no risk. Note this is an affiliate link, so if you end up signing up for a paid plan, I will get a small commission at no cost to you, to help fund the cost of publishing this free newsletter.
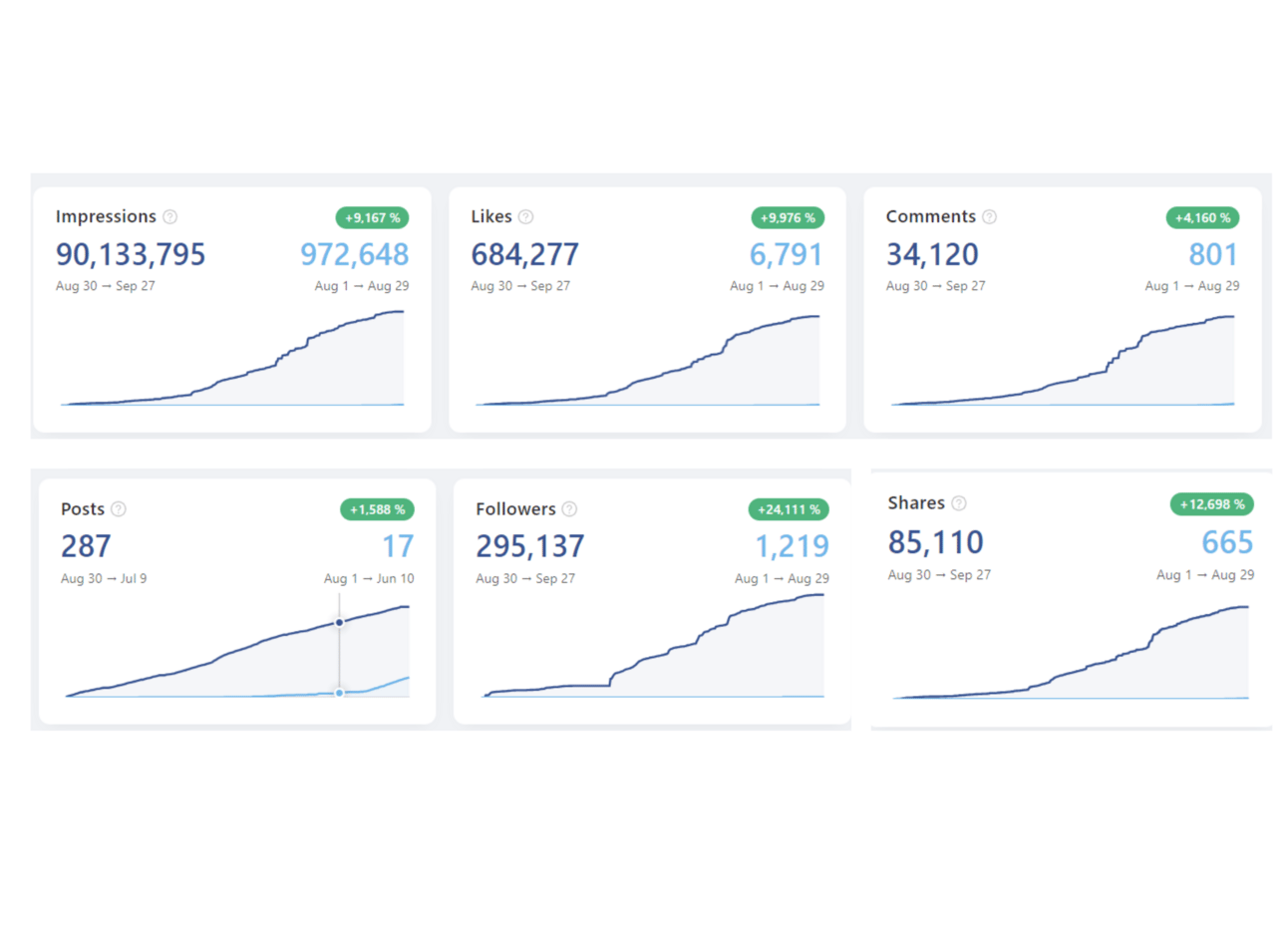
Curious what my Shield Dashboard looks like for the past 365 days?
Have a look:
New this week
I use Thinkific to power up The Cash Flow Masterclass and the several upcoming courses I have in the works. Download the new Thinkific mobile app and access my courses anywhere, anytime — on any device.
For Upcoming Course Launches, Promotions, Private Sales and Free Finance Webinars, sign up here.
New pricing options are available for The Cash Flow Masterclass to make it more affordable than ever to get strategic cash flow education.
The Finance Gem 💎 Referral Program is here - share this newsletter with your network and earn rewards! Scroll down to find out more!
Reading for the first time? Please Subscribe here.
Now let’s get into this week’s strategic finance insights:
You’re probably using EBITDA wrong
Because EBITDA has 10 Major Problems you should be aware of.
Learn what they are so you can keep yourself and your business out of trouble.
1️⃣ Ignoring Capital Expenditures
☑️ EBITDA excludes capital expenditures, potentially masking how capital-intensive a business really is.
➡️ Employ Free Cash Flow metrics, which include both operating cash flow and capital investment cashflow, to assess EBITDA on a cash basis.
➡️ Particularly crucial for asset-heavy sectors like manufacturing and utilities.
2️⃣ Overlooking Debt Service
☑️ EBITDA disregards interest costs, underplaying the true financial burden of debt capital.
➡️ Use Interest Coverage Ratio and Debt Coverage Ratio to assess how comfortably a business can handle its debt obligations
➡️ Especially critical when assessing leveraged buyouts or refinancing options.
3️⃣ Neglecting Working Capital
☑️ EBITDA doesn't factor in changes in working capital, which may impact cash availability.
➡️ Analyze the Cash Conversion Cycle to gain insights into how efficiently a company is converting resources into cash.
➡️ Particularly useful for high-growth companies.
4️⃣ Not Accounting for Non-Operating Items
☑️ EBITDA can often become distorted by non-operating income or costs which distract from the true operating performance.
➡️ Focus on Operating Income to better understand the core business performance, stripping out investment or one-time income sources outside the core business operations.
5️⃣ No Depreciation and Amortization Factor
☑️ EBITDA ignores depreciation and amortization, potentially making older, fully-depreciated assets seem more profitable.
➡️ Complement EBITDA with Asset Turnover Ratio to gauge how efficiently assets are being utilized
➡️ Especially relevant for industries with significant tangible assets.
6️⃣ Valuation Mistakes
☑️ EBITDA can easily inflate the perceived value of a business by ignoring critical costs.
➡️ Use EV/EBITDA for valuation, but always cross-verify with DCF analyses, comps and other metrics such as P/E and P/B ratios
7️⃣ Ignoring Geographic Variability
☑️ EBITDA doesn't account for costs and regulations that vary by region, less useful for multinational companies.
➡️ Break down EBITDA by region or business unit to reflect local economic conditions, tax rates, and even the competitive environment.
8️⃣ Failing to Adjust for One-Time Items
☑️ EBITDA can include one-time gains or losses, impacting the interpretation of ongoing profitability.
➡️ Manually adjust for these items to arrive at a normalized EBITDA, especially during due diligence for mergers or acquisitions or during performance evaluations that drive executive compensation
9️⃣ Being Misled by Financial Engineering
☑️ Companies can manipulate EBITDA figures through financial engineering, creating an overly optimistic financial picture.
➡️ Reconcile EBITDA back to GAAP figures and scrutinize any reconciliation adjustments.
➡️ Pay close attention to any large or consistent "add-backs" that inflate EBITDA, for which there may or may not be reasonable explanations
🔟 Comparing Apples to Oranges
☑️ EBITDA can mislead when comparing companies in different industries or stages of growth due to varying capital needs and financing structures.
➡️ Utilize industry-specific ratios and maturity-stage benchmarks for a more appropriate comparison (
➡️ For example, EBITDA margin for SaaS companies versus manufacturing firms will vary greatly
10 Business Finance Strategies
Business needs Capital to grow.
Capital needs Returns to accept the repayment Risk.
The higher the Risk, the higher the Capital Returns required.
From Low Risk/Low Return Capital to High Risk High/Return Capital
Here are the most common sources of Capital to fund your business growth.
Remember that the business financing strategies at your disposal are heavily dependent on your:
🎯 business life stage
🎯 business growth prospects
🎯 business risk profile
The right mix of financing can transform your business growth trajectory by optimizing the mix of debt and equity used to fund your operation for the specific strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of the company.
Here are the most critical 10 strategies to consider:
1️⃣ Equity Financing
☑️ Venture Capital: Ideal for startups with high growth prospects, providing essential funding for scaling. Downsides include dilution of ownership and some loss of control.
☑️ Angel Investment: Suitable for early-stage companies needing moderate capital. More flexible terms and potential mentorship are perks, though funding is generally less than VC.
☑️ IPO (Initial Public Offering): Great for companies seeking significant capital, but comes with high costs, regulatory hurdles, and ongoing disclosure requirements.
2️⃣ Debt Financing
☑️ Bank Loans: Traditional loans against collateral are good for maintaining company control but come with strict repayment terms.
☑️ Corporate Bonds: Allows sizable fundraising without ownership dilution, but may entail high-interest payments.
☑️ Lines of Credit: Useful for managing short-term liquidity needs, generally at lower interest rates than credit cards but may require collateral.
3️⃣ Hybrid Instruments
☑️ Convertible Debt: Initial debt can convert to equity at a later stage, offering downside protection for investors and valuation flexibility for founders.
☑️ Mezzanine Financing: A blend of debt and equity features, useful for acquisitions or rapid scaling but usually comes at higher interest rates.
4️⃣ Internal Financing
☑️ Retained Earnings: Involves reinvesting profits back into the company. A zero-cost, non-dilutive approach but may represent an opportunity cost.
☑️ Working Capital Optimization: Enhances liquidity by efficient management of accounts receivable, payable, and inventory, without needing external funds.
5️⃣ Government and Institutional Financing
☑️ Grants: Provides non-dilutive funding with usage restrictions and is typically competitive.
☑️ SBA Loans: More lenient than traditional loans and often government-backed, but entail a slow and paperwork-heavy process.
☑️ R&D Tax Credits: Tax offsets for qualifying R&D activities, sometimes resulting in cash refunds.
6️⃣ Trade Financing
☑️ Supplier Credit: Extending payment terms with suppliers aids cash flow but requires good supplier relations.
☑️ Invoice Factoring: Quick liquidity by selling accounts receivables, usually at a discount.
☑️ Trade Credit Insurance: Insures against non-payment risks, facilitating other financing options.
☑️ Bank Letter of Credit (LCs): Facilitates international trade by guaranteeing payments, though it comes with fees.
☑️ Bank Letters of Guarantees (LGs): Ensures performance or payment, often requiring collateral, and is useful for contracts and leasing.
7️⃣ Strategic Alliances and Joint Ventures
☑️ Licensing: Monetizes intellectual property through licensing agreements, generating upfront fees or royalties.
☑️ Strategic Investments: Partnerships for mutual benefits, including financial and operational advantages such as market access or cost-sharing.
8️⃣ Off-balance-sheet Financing
☑️ Operating Leases: Short-term asset leasing improves financial ratios but requires navigating complex accounting rules.
☑️ Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs): Isolates financial risks and enhances liquidity by off-loading assets, but needs strict oversight.
9️⃣ Asset-based Financing
☑️ Sale and Leaseback: Converts owned assets into leased assets for quick capital while retaining usage rights.
☑️ Inventory Financing: Short-term loans or lines of credit secured by inventory, useful for immediate funding needs.
🔟 Foreign Exchange and Hedging Strategies
☑️ Currency Swaps: Manages foreign currency exposure by exchanging currencies with a counterparty for a specified period.
☑️ Forwards: Contracts to buy or sell currencies at future dates at predetermined rates, effective for hedging.
☑️ Interest Rate Swaps: Exchanges interest rate obligations between two parties, useful for managing variable interest rate risks.
EBITDA is not Cash Flow
So don’t use it as a “proxy” for cash flow.
Don’t do deals on “multiples” alone.
And don’t be fooled by randomness.
There’s no substitute for hard work, DCFs and Quality of Earnings.
Here are 10 things you need to know:
1// “EBITDA” is a profitability measure, essentially accounting (operating) profit with interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization added back to it.
☑️It’s claim to fame is that it can be used to analyze and compare profitability between companies and industries because it eliminates the effects of financing, taxes, and accounting policy choices.
2// “Operating Cash Flow” or “OCF” is a flow measure of the amount of cash generated by your business operations
☑️It’s calculated (indirectly) by adjusting net income for depreciation, amortization, and other non-cash expenses, as well as for the amount of cash trapped or released by your current assets and current liabilities.
3// Both EBITDA and OCF add back depreciation and amortization.
☑️ However, unlike EBITDA which never looks at depreciation and amortization again, OCF simply adjusts these items out, so that Investing Cash Flows can better capture them as part of the cash flow actually spent (or gained) in transactions involving fixed assets.
4// EBITDA does not eliminate operating non-cash expenditures like stock based compensation, provisions and reserves (but it wishes it did, hence why adjusted EBITDAs are so popular)
☑️You may have incurred these expenses in the current period and correspondingly reported reduced Net Income and Retained Earnings, but your cash balances weren’t also impacted and OCF will capture that.
5// EBITDA does not include the tax you actually paid during the period.
☑️ While every company’s tax circumstances differ based on a multitude of factors, your taxes paid represent a cash payment that reduced your cash available for other uses, and this will be reflected in OCF.
6// EBITDA does not consider the cash trapped or released inside your working capital accounts.
☑️ Working capital accounts like Accounts Receivable, Accounts Payable, Inventory and Prepaid Expenses can absorb a substantial amount of the revenues earned in the period, which would drop your cash balances despite posting strong Income and EBITDA.
☑️ Alternatively, working capital accounts can also release a substantial amount of cash into your business, distracting from the fact it may have incurred operating losses during that period.
7// EBITDA does not include the interest expense incurred and paid by your business in the current period on account of borrowing capital.
☑️ While every company’s capital structure differs based on their individual financing choices, your interest paid (as opposed to interest accrued but not paid) does represent a cash payment which reduces your cash available for other uses, and OCF will capture that.
8// EBITDA will frequently exclude foreign exchange losses on the claim that they are non-operating and non-recurring (hence why they’ll be listed below the line as part of non-operating expenses).
☑️ There may well be several circumstances where the impact of foreign exchange transactions could be deemed non-operating in nature, such as following a one-off acquisition or an asset purchase.
☑️ However, none of that changes the fact your FX gains and losses directly impact your cash balance and OCF will capture that while EBITDA may not.
9// EBITDA will frequently exclude severance and reorganization costs, also under the claim that they are non-operating in nature (and non-recurring).
☑️ While these costs may indeed not be expected to reoccur in the foreseeable future, they do represent a cash payment which reduce your cash available for other uses, which is going to be reflected into the OCF but possibly not in your EBITDA.
10// EBITDA will mostly exclude grant and other similar type of extraordinary income on the claim that they are non-operating in nature and thus should be excluded from operating profits.
☑️ While these sources of income may not be a direct result of your commercial trade activity, they are still a result of indirect operating activities and they represent inflows that increase your available cash balances; this will be reflected into the OCF but likely not in your EBITDA.


If you’re still unsure if my Cash Flow Masterclass is for you, consider this:
☑️ It’s GOOD: you will learn from one of the best coaches - a CPA, MBA with unique expertise in corporate and commercial finance, financial and managerial accounting, business management and business strategy.
☑️ It’s FAST: it takes less than 2 hours to breeze through the course on any device, and you can pause anytime
☑️ It’s PRACTICAL: you get dynamic financial models included in the course and you will be applying what you learn for the rest of your career
☑️ It’s VALUABLE: the course cost is nominal compared to the value it provides for your career, and there are several payment plans available
☑️ It’s YOURS: you get lifetime access on any device (audio mode available in the app)
☑️ It’s EXPENSIBLE: your employer or business can reimburse you, making this a win-win purchase for you and your organization.
ENROLL TODAY - your Career and your Organization will thank you!
Costs vs. Expenses
Here’s what you need to know.
🎯 Costs represent the monetary value of resources spent to create or acquire an asset.
☑️ Raw materials, labor, manufacturing overhead
☑️ Financial Statements Impact: Primarily affect the Balance Sheet as assets, move to Income Statement when recognized as Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
🎯 Expenses represent the consumption of assets or the incurring of liabilities during regular business operations.
☑️ Rent, utilities, marketing
☑️ Financial Statements: Primarily affect the Income Statement under "Operating Expenses."
🎯 What makes these concepts complicated and confusing?
Their recognition.
☑️ Cost Recognition Challenges: Deciding when costs should be capitalized (as an asset) or expensed (as COGS or depreciation expense).
Use judgement in the application of standardized accounting principles (GAAP/IFRS) for items like R&D, software development.
☑️ Expense Recognition Challenges: Timing of recognition, especially for prepaid or deferred expenses.
Use accrual accounting; matching principle to align expenses with associated revenues.
🎯 What are their Tax Implications?
Costs >>> Capital Expenditures
Can be depreciated over the asset's useful life.
Depreciation provides a reduction in taxable income, offering a "tax shield."
Costs >>> Product Expenditures (Inventoriable Costs)
Impact the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) on the Income Statement.
Higher COGS reduces gross profit, which subsequently reduces taxable income.
Expenses >>> Operating Expenses
These are regular costs tied to the daily operation of the business.
Typically deductible from revenue in the same period they're incurred
🎯 Strategic Decision-Making
☑️ Costs have long-term implications
High fixed costs result in increased operating leverage, which means that profitability will be more sensitive to changes in sales volumes.
☑️ Expenses have shorter term implications, enabling more flexibility and adaptability
Immediate impact on profitability and cash flow
☑️ Both are challenged by Capitalizing vs. Expensing decisions which can be complex to make and dramatically impact EBITDA, taxes and valuations (research expenditures, prepaid expenses)

13 Best Business Books
Every Business Decision is a Finance Decision.
Source Debt & Equity Capital.
Invest Capital into Assets.
Increase Capital.
Return Capital.
Reinvest.
Repeat.
Here is a full MBA curriculum with 13 Best Business Books to round up your business knowledge without the price tag of an MBA.
Referral Program
If you’re enjoying this newsletter, please forward it to a friend. It only takes 3 seconds. Writing this took 4 hours.
🎯Refer 5 people and get my exclusive eBook 10 Essential Strategic Finance Concepts that link Accounting, Finance and Strategy
🎯Refer 10 people and get an exclusive $10 Off coupon for your favorite infographic in my digital store.
Poll Time
How did it feel reading this week's issue?
As always, if you have suggestions or feedback, simply reply to this email.
Looking for More ?
Upgrade your strategic finance skills with The Cash Flow Masterclass, my highly reviewed, on-demand video course.
Work with me. Tap into my 20+ years of strategic finance & business intelligence, and get coaching for your own career. Availability is very limited. Book here.
Get growth business advisory for your organization with short, medium and long term financial planning, and big-picture financial models so you’re always finance-ready. Reach out here.
Sponsor a future issue of The Finance Gem 💎 or hire me to guest speak in your events and webinars
Train your team on strategic finance concepts and elevate their knowledge, decision-making and productivity. Reach out here.
Thanks so much for reading. See you next week.
Oana

: